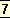
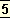
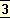

Sri Aurobindo
The Harmony of Virtue
Early Cultural Writings — 1890-1910
Karmayogin: A Weekly Review
Saturday 3rd July 1909 — No.3
Yoga and Human Evolution
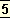
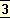

The whole burden of our human progress has been an attempt to escape from the bondage to the body and the vital impulses.
According to the scientific theory, the human being began as the animal, developed through the savage and consummated in the modern civilized1 man.
The Indian theory is different.
God created the world by developing the many out of the One and the material out of the spiritual.
From the beginning, the objects which compose the physical world were arranged by Him in their causes, developed under the law of their being in the subtle or psychical world and then manifested in the gross or material world.
From kāraṇa to sūkṣma, from sūkṣma to sthūla, and back again, that is the formula.
Once manifested in matter, the world proceeds by laws which do not change from age to age, by a regular succession, until it is all withdrawn back again into the source from which it came.
The material goes back to2 the psychical and the psychical is involved in the3 cause or seed.
It is again put out when the period of expansion recurs and runs its course on similar lines but with different details till the period of contraction is due.
Hinduism regards the world as a recurrent series of phenomena of which the terms vary but the general formula abides the same.
The theory is only acceptable if we recognise the truth of the conception formulated in the Vishnu Purana of the world as vijñānavijṛmbhitāni, developed4 of ideas in the Universal Intelligence which lies at the root of all material phenomena and by its indwelling force shapes the growth of the tree and the evolution of the clod as well as the development of living creatures and the progress of mankind.
Whichever theory we take, the laws of the material world are not affected.
From aeon to aeon, from kalpa to kalpa Narayan manifests himself in an ever-evolving humanity which grows in experience by a series of expansions and contractions towards its destined self-realisation in God.
That evolution is not denied by the Hindu theory of yugas.
Each age in the Hindu system has its own line 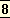
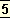
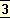
 of moral and spiritual evolution and the decline of the dharma or established law of conduct from the satya to the kaliyuga is not in reality a deterioration but a detrition of the outward forms and props of spirituality in order to prepare a deeper spiritual intensity within the heart.
In each kaliyuga mankind gains something in essential spirituality.
Whether we take the modern scientific or the ancient Hindu standpoint the progress of humanity is a fact.
The wheel of Brahma rotates for ever but it does not turn in the same place; its rotations carry it forward.
of moral and spiritual evolution and the decline of the dharma or established law of conduct from the satya to the kaliyuga is not in reality a deterioration but a detrition of the outward forms and props of spirituality in order to prepare a deeper spiritual intensity within the heart.
In each kaliyuga mankind gains something in essential spirituality.
Whether we take the modern scientific or the ancient Hindu standpoint the progress of humanity is a fact.
The wheel of Brahma rotates for ever but it does not turn in the same place; its rotations carry it forward.
The animal is distinguished from man by its enslavement to the body and the vital impulses.
Aśanāyā mṛtyuḥ, Hunger who is Death, evolved the material world from of old, and it is the physical hunger and desire and the vital sensations and primary emotions connected with the prāṇa that seek to feed upon the world in the beast and in the savage man who approximates to the condition of the beast.
Out of this animal state, according to European Science, man rises working out the tiger and the ape by intellectual and moral development in the social condition.
If the beast has to be worked out, it is obvious that the body and the prāṇa must be conquered, and as that conquest is more or less complete, the man is more or less evolved.
The progress of mankind has been placed by many predominatingly in the development of the human intellect, and intellectual development is no doubt essential to self-conquest.
The animal and the savage are bound by the body because the ideas of the animal or the ideas of the savage are mostly limited to those sensations and associations which are connected with the body.
The development of intellect enables a man to find the deeper self within and partially replace what our philosophy calls the dehātmakabuddhi, the sum of ideas and sensations which make us think of the body as ourself, by another set of ideas which reach beyond the body, and existing for their own delight and substituting intellectual and moral satisfaction as the chief objects of life, master, if they cannot entirely silence, the clamour of the lower sensual desires.
That animal ignorance which is engrossed with the cares and the pleasures of the body and the vital impulses, emotions and sensations is tāmasika, the result of the predominance of the third principle of nature which leads to ignorance and inertia.
That 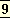
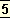
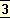
 is the state of the animal and the lower forms of humanity which are called in the Purana the first or tāmasika creation.
This animal ignorance, the development of the intellect tends to dispel and it assumes therefore an all-important place in human evolution.
is the state of the animal and the lower forms of humanity which are called in the Purana the first or tāmasika creation.
This animal ignorance, the development of the intellect tends to dispel and it assumes therefore an all-important place in human evolution.
But it is not only through the intellect that man rises. If the clarified intellect is not supported by purified emotions, the intellect tends to be dominated once more by the body and to put itself at its service and the leadership5 of the body over the whole man becomes more dangerous than in the natural state because the innocence of the natural state is lost. The power of knowledge is placed at the disposal of the senses, sattva serves tamas, the god in us becomes the slave of the brute. The disservice which scientific materialism is unintentionally doing the world is to encourage a return to this condition; the suddenly awakened masses of men, unaccustomed to deal intellectually with ideas, able to grasp the broad attractive innovations of free thought but unable to appreciate its delicate reservations, verge towards that reeling back into the beast, that relapse into barbarism which was the condition of the Roman Empire at a high stage of material civilization6 and intellectual culture and which a distinguished British Statesman declared to be7 the condition to which all Europe approached. The development of the emotions is therefore the first condition of a sound human evolution. Unless the feelings tend away from the body and the love of others take8 increasingly the place of the brute love of self, there can be no progress upward. The organisation of human society tends to develop the altruistic element in man which makes for life and battles with and conquers aśanāyā mṛtyuḥ. It is therefore not the struggle for life, or at least not the struggle for our own life, but the struggle for the life of others which is the most important term in evolution, — for our children, for our family, for our class, for our community, for our race and nation, for humanity. An everlasting9 self takes the place of the old narrow self which is confined to our individual mind and body and it is this moral growth which society helps and organises.
So far there is little essential difference between our own ideas of human progress and those of the West, except in this 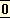
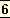
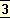
 vital point that the West believes this evolution to be a development of matter and the satisfaction of the reason, the reflective and observing intellect, to be the highest term of our progress.
Here it is that our religion parts company with Science.
It declares the evolution to be a conquest of matter by the recovery of the deeper emotional and intellectual self which was involved in the body and overclouded by the desires of the prāṇa.
In the language of the Upanishads the manaḥkoṣa and the buddhikoṣa are more than the prāṇakoṣa and annakoṣa and it is to them that man rises in his evolution.
Religion further10 seeks a higher term for our evolution than the purified emotions or the clarified activity of the observing and reflecting intellect.
The highest term of evolution is the spirit in which knowledge, love and action, the three-fold dharma of humanity, find their fulfilment and end.
This is the ātman in the ānandakoṣa, and it is by communion and identity of this individual self with the universal self which is God that man will become entirely pure, entirely strong, entirely wise and entirely blissful, and the evolution will be fulfilled.
The conquest of the body and the vital self by the purification of the emotions and the clarification of the intellect was the principal work of the past.
The purification has been done by morality and religion, the clarification by science and philosophy, art, literature and social and political life being the chief media in which these uplifting forces have worked.
The conquest of the emotions and the intellect by the spirit is the work of the future.
Yoga is the means by which that conquest becomes possible.
vital point that the West believes this evolution to be a development of matter and the satisfaction of the reason, the reflective and observing intellect, to be the highest term of our progress.
Here it is that our religion parts company with Science.
It declares the evolution to be a conquest of matter by the recovery of the deeper emotional and intellectual self which was involved in the body and overclouded by the desires of the prāṇa.
In the language of the Upanishads the manaḥkoṣa and the buddhikoṣa are more than the prāṇakoṣa and annakoṣa and it is to them that man rises in his evolution.
Religion further10 seeks a higher term for our evolution than the purified emotions or the clarified activity of the observing and reflecting intellect.
The highest term of evolution is the spirit in which knowledge, love and action, the three-fold dharma of humanity, find their fulfilment and end.
This is the ātman in the ānandakoṣa, and it is by communion and identity of this individual self with the universal self which is God that man will become entirely pure, entirely strong, entirely wise and entirely blissful, and the evolution will be fulfilled.
The conquest of the body and the vital self by the purification of the emotions and the clarification of the intellect was the principal work of the past.
The purification has been done by morality and religion, the clarification by science and philosophy, art, literature and social and political life being the chief media in which these uplifting forces have worked.
The conquest of the emotions and the intellect by the spirit is the work of the future.
Yoga is the means by which that conquest becomes possible.
In Yoga the whole past progress of humanity, a progress which it holds on a very uncertain base11, is rapidly summed up, confirmed and made an inalienable possession.
The body is conquered, not imperfectly as by the ordinary civilised man, but entirely.
The vital part is purified and made the instrument of the higher emotional and intellectual self in its relations with the outer world.
The ideas which go outward are replaced by the ideas which move within, the baser qualities are worked out of the system and replaced by those which are higher, the lower emotions are crowded out by the nobler.
Finally all ideas and emotions are stilled and by the perfect awakening of the intuitive 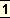
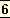
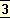
 reason which places mind in communion with spirit the whole man is ultimately placed at the service of the Infinite.
All false self merges into the true self.
Man acquires likeness, union or identification with God.
This is Mukti, the state in which humanity thoroughly realises the freedom and immortality which are its eternal goal.
reason which places mind in communion with spirit the whole man is ultimately placed at the service of the Infinite.
All false self merges into the true self.
Man acquires likeness, union or identification with God.
This is Mukti, the state in which humanity thoroughly realises the freedom and immortality which are its eternal goal.
Later edition of this work: The Complete Works of Sri Aurobindo.- Set in 37 volumes.- Volume 13.- Essays in Philosophy and Yoga: Shorter Works. 1910 – 1950.- Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 1998.- 604 p.
1 1998 ed.: civilised
2 1998 ed.: into
3 1998 ed.: its
4 1998 ed.: developments
5 1998 ed.: lordship
6 1998 ed.: civilisation
7 1998 ed.: declared the other day to be
8 1998 ed.: takes
9 1998 ed.: ever-enlarging
10 1998 ed.: farther
11 1998 ed.: lease