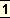
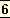
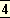

Sri Aurobindo
The Harmony of Virtue
Early Cultural Writings — 1890-1910
Epistles from Abroad [3]
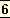
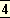

Your list of questions is rather a long one.
I will answer you in the mass rather than in detail; and chiefly I will attack two fallacies with which your letter teems, if I may use such an expression, and which lie at the root of your very disfavourable attitude.
There are two Hinduisms; one which takes its stand on the kitchen and seeks its Paradise by cleaning the body; another which seeks God, not through the cooking pot and the social convention, but in the soul.
The latter is also Hinduism and it is a good deal older and more enduring than the other; it is the Hinduism of Bhishma and Srikrishna, of Shankara and Chaitanya, the Hinduism which exceeds Hindusthan, was from of old and will be for ever, because it grows eternally through the aeons.
Its watchword is not kriyā, but karma; not śāstra, but jñānam; not ācāra, but bhakti.
Yet it accepts kriyā, śāstra and ācāra, not as ends to be followed for their own sake, but as means to perfect karma, jñāna and bhakti.
Kriyā in its1 dictionary means every practice which helps the gaining of higher knowledge, such as the mastering of the breath, the repetition of the Mantra, the habitual use of the Name, the daily meditation on the idea.
By śāstra it means the knowledge which regulates karma, which fixes the kartavyam and the akartavyam, that which should be done and that which should not, and it recognizes2 two sources of that knowledge, — the eternal wisdom, as distinct from the temporary injunctions in our ancient books and the book that is written by God in the human heart, the eternal and apauruṣeya Veda.
By ācāra it understands all moral discipline by which the heart is purified and made a fit vessel for divine love.
There are certain kriyās, certain rules of śāstra, certain details of ācāra, which are for all time and of perpetual application; there are others which are temporary, changing with the variation of deśa, kāla and pātra, time, place and needs3 of humanity.
Among 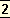
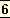
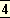
 the temporary laws the cooking pot and the lustration had their place, but they are not for all, nor for ever.
It was in a time of calamity, of contraction, under external pressure that Hinduism fled from the inner temple and hid itself in the kitchen.
the temporary laws the cooking pot and the lustration had their place, but they are not for all, nor for ever.
It was in a time of calamity, of contraction, under external pressure that Hinduism fled from the inner temple and hid itself in the kitchen.
The higher and truer Hinduism is also of two kinds, sectarian and unsectarian, disruptive and synthetic, that which binds itself up in the aspect and that which seeks the All. The first is born of rajasic or tamasic attachment to an idea, an experience, an opinion or set of opinions, a temperament, an attitude, a particular Guru, a chosen Avatar. This attachment is intolerant, arrogant, proud of a little knowledge, scornful of knowledge that is not its own. It is always talking of the ku-saṃskāras, superstitions, of others and is blind to its own; or it says, “My Guru is the only Guru, and all others are either charlatans or inferior,” or, “My temperament is the right temperament, and those who do not follow my path are fools or pedants or insincere,” or “My Avatar is the real God Himself and all the others are only lesser revelations;” or “My iṣṭadevatā is God, the others are only His partial manifestations.” When the soul rises higher, it follows by preference its own ideas, experiences, opinions, temperament, Guru, iṣṭa, but it does not turn an ignorant and exclusive eye upon others. “There are many paths,” it cries, “and all lead equally to God. All men, even the sinner and the atheist are my brothers in Sadhana and the Beloved is drawing them each in His own way to the One without a second.” But when the full knowledge dawns, I embrace all experiences in myself, I know all ideas to be true, all opinions useful, all experiences and attitudes means and stages in the acquisition of universal experience and completeness, all Gurus imperfect channels or incarnations of the one and only Teacher, all iṣṭas and Avatars to be God Himself.
That is what Ramakrishna taught by His life and Sadhana and therefore is He the Avatar of the age, the One who prepares the future of humanity.
But there is a danger of turning Him into the Guru of a sect, the incarnate God of a dogmatic religion, to stultify His own life and teachings by making Him the object of a narrow attachment, an intolerant reverence, a sectarian worship.
That must be avoided.
It is the great curse which attends 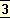
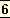
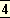
 the organisation of religion.
Let us have done with sects and churches and worship God only.
the organisation of religion.
Let us have done with sects and churches and worship God only.
The destruction of bondage, the realisation of freedom, the trampling upon our fetters, that is the first need of the future. It was to give mukti that Ramakrishna came, not to impose a new bondage. Therefore was Vivekananda His Apostle to the Gentiles, a man who in all things asserted freedom. The soul of Hinduism languishes in an unfit body. Break the mould that the soul may live. Is it not the first teaching of Yoga to destroy the dehātmaka-buddhi, the blindness that identifies the soul with its temporary body? If the body were young, adaptable, fit, the liberated soul might use it, but it is decrepit, full of ill-health and impurity. It must be changed, not by the spirit of Western iconoclasm which destroys the soul with the body, but by national Yoga.
Circa 1910
Later edition of this work: The Complete Works of Sri Aurobindo.- Set in 37 volumes.- Volume 1.- Early Cultural Writings (1890 — 1910).- Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 2003.- 784 p.
1 2003 ed.: the
2 2003 ed.: recognises
3 2003 ed.: and the needs