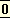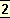Sri Aurobindo
Early Cultural Writings
(1890 — 1910)
Part Two. On Literature
The Poetry of Kalidasa
Hindu Drama [2]
Deftness1 and strength in dialogue, masterly workmanship in plot-making and dramatic situation and vital force of dramatic poetry are enough in themselves to make a fine and effective poetical play for the stage, but for a really great drama a farther and rarer gift is needed, the gift of dramatic characterisation.
This power bases itself in its different degrees sometimes on2 great experience of human life, sometimes on a keen power of observation and accurate imagination making much matter out of a small circle of experience but in its richest possessors on a boundless sympathy with all kinds of humanity accompanied by a power of imbibing and afterwards of selecting and bringing out from oneself at will impressions received from others3.
This supreme power, European scholars agree, is wanting in Hindu dramatic literature.
A mere poet like Goethe may extend unstinted and even superlative4 praise to a Shacountala but the wiser critical and scholarly mind passes a far less favourable verdict; there is much art in Hindu poetry, it is said, but no genius; there is plenty of fancy but no imagination; beautiful and even moving poetry is abundant, but the characters are nil; the
colouring is rich but colour is all5.
Indian scholars trained in our schools to repeat6 what they have learnt do not hesitate to add their voice to the chorus7.
A Hindu scholar of acute diligence and wide Sanscrit learning has even argued that the Hindu mind is constitutionally incapable of original and living creation; he has alleged the gigantic, living and vigorous personalities of the Mahabharat8 as an argument to prove that these characters must have been real men and women, copied from the life; since no Hindu poet could have created character with such truth and power.
On the other side the Bengali critics, men of no mean literary taste and perception though inferior in pure verbal scholarship, are agreed in regarding the characters of Kalidasa and Bhavabhuti as beautiful and energetic creations, not less deserving of study than the9 personalities10 of Elizabethan11 drama.
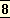
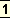
 This contradiction, violent as it is, is not difficult to understand, since it takes its root in an element always more or less present in criticism, the national element.
National character12, national prejudices, national training preordain for the bulk of us the spirit in which we shall approach13 unfamiliar poetry.
Now the average English mind is capable of appreciating character as manifested in strong action or powerfully revealing speech, but constitutionally dull to the subtleties of civilized14 character15 which have their theatre in the mind and the heart and make of a slight word, a gesture or even silence their sufficient revelation.
The nations of Europe, taken in the mass, are still semicivilized; their mind feeds on the physical, external and grossly salient features of life; where there is no brilliance and glare, they are apt to condemn the personality16 as characterless.
A strength that shuns ostentation, a charm that is not luxuriant, not naked to the first glance, are appreciable only to the few select minds who have chastened their natural leanings by a wide and deep culture.
The Hindu on his side distastes17 violence in action, excess in speech, ostentation or effusiveness in manner; he demands from his ideal temperance and restraint as well as nobility, truth and beneficence; the Aryan or true gentleman must be मिताचारः (mitācāraḥ) and मितभाषी, (mitābhāṣī) restrained in action and temperate in speech.
This contradiction, violent as it is, is not difficult to understand, since it takes its root in an element always more or less present in criticism, the national element.
National character12, national prejudices, national training preordain for the bulk of us the spirit in which we shall approach13 unfamiliar poetry.
Now the average English mind is capable of appreciating character as manifested in strong action or powerfully revealing speech, but constitutionally dull to the subtleties of civilized14 character15 which have their theatre in the mind and the heart and make of a slight word, a gesture or even silence their sufficient revelation.
The nations of Europe, taken in the mass, are still semicivilized; their mind feeds on the physical, external and grossly salient features of life; where there is no brilliance and glare, they are apt to condemn the personality16 as characterless.
A strength that shuns ostentation, a charm that is not luxuriant, not naked to the first glance, are appreciable only to the few select minds who have chastened their natural leanings by a wide and deep culture.
The Hindu on his side distastes17 violence in action, excess in speech, ostentation or effusiveness in manner; he demands from his ideal temperance and restraint as well as nobility, truth and beneficence; the Aryan or true gentleman must be मिताचारः (mitācāraḥ) and मितभाषी, (mitābhāṣī) restrained in action and temperate in speech.
This national tendency shows itself even in our most vehement work.
The Mahabharat18 is that19 section of our literature which deals most with the external and physical and corresponds best to the European idea of the epic; yet the intellectualism of even the Mahabharat20, its preference of mind-issues to physical and emotional collisions and catastrophes, its continual suffusion of these when they occur with mind and ideality, the civilisation, depth and lack of mere sensational turbulence, in one word the Aryan cast of its characters, are irritating to European21 scholars.
Thus a historian of Indian literature complains that Bhema22 is the one really23 epic character in this poem.
He meant, evidently, the one24 character in which vast and irresistible strength, ungovernable impetuousness of passion, warlike fury and destroying anger are grandiosely displayed25.
But to the Hindu, whose ideas of epic are not coloured with the wrath of Achilles, 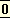
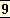
 epic motive and character are not confined to what is impetuous, huge and untamed; he demands a larger field for the epic and does not confine it to savage and half savage epochs.
Gentleness, patience, self-sacrifice, purity, the civilized26 virtues, appear to him as capable of epic treatment as martial fire, brute strength, revenge, anger, hate and ungovernable self-will.
Rama mildly and purely renouncing the empire of the world for the sake of his father’s honour seems to them as epic and mighty a figure as Bhema27 destroying Kechaka28 in his wild fury of triumphant strength and hatred.
It is noteworthy that the European temperament finds vice more interesting than virtue, and in its heart of hearts damns the Christian qualities with faint praise as negative, not positive virtues; the difficulty European writers experience in making good men sympathetic is a commonplace of literary observation.
In all these respects the Hindu attitude is diametrically opposed to the European.
This attitude of the Hindu mind as evinced in the Mahabharata is so intolerable to European scholars that they have been forced to ease their irritation by conjuring up the phantom of an original ballad-epic more like their notions of what an epic should be, an epic in which the wicked characters of the present Mahabharata were the heroes and the divine champions of right of the present Mahabharata were the villains!
The present Mahabharata is, they say, a sanctimonious monastic corruption of the old vigorous and half-savage poem.
To the Hindu the theory naturally seems a grotesque perversion of ingenuity but its very grotesqueness is eloquent of the soil it springs from, the soil of the half barbarous temperament of the martial29 and industrial Teuton which cannot, even when civilised, entirely sympathise with the intellectual working of more radically civilised types.
This fundamental difference of outlook on character, generating difference in critical appreciation of dramatic and epic characterisation is of general application, but it acquires a peculiar force when we come to consider the Hindu drama; for here the ingrained disparity is emphasized30 by external conditions.
epic motive and character are not confined to what is impetuous, huge and untamed; he demands a larger field for the epic and does not confine it to savage and half savage epochs.
Gentleness, patience, self-sacrifice, purity, the civilized26 virtues, appear to him as capable of epic treatment as martial fire, brute strength, revenge, anger, hate and ungovernable self-will.
Rama mildly and purely renouncing the empire of the world for the sake of his father’s honour seems to them as epic and mighty a figure as Bhema27 destroying Kechaka28 in his wild fury of triumphant strength and hatred.
It is noteworthy that the European temperament finds vice more interesting than virtue, and in its heart of hearts damns the Christian qualities with faint praise as negative, not positive virtues; the difficulty European writers experience in making good men sympathetic is a commonplace of literary observation.
In all these respects the Hindu attitude is diametrically opposed to the European.
This attitude of the Hindu mind as evinced in the Mahabharata is so intolerable to European scholars that they have been forced to ease their irritation by conjuring up the phantom of an original ballad-epic more like their notions of what an epic should be, an epic in which the wicked characters of the present Mahabharata were the heroes and the divine champions of right of the present Mahabharata were the villains!
The present Mahabharata is, they say, a sanctimonious monastic corruption of the old vigorous and half-savage poem.
To the Hindu the theory naturally seems a grotesque perversion of ingenuity but its very grotesqueness is eloquent of the soil it springs from, the soil of the half barbarous temperament of the martial29 and industrial Teuton which cannot, even when civilised, entirely sympathise with the intellectual working of more radically civilised types.
This fundamental difference of outlook on character, generating difference in critical appreciation of dramatic and epic characterisation is of general application, but it acquires a peculiar force when we come to consider the Hindu drama; for here the ingrained disparity is emphasized30 by external conditions.
It has been pointed out, perhaps too often, that31 the Hindu drama presents some32 remarkable points of contact with the 
 Elizabethan.
In the mixture of prose and poetry, in the complete freedom with which time and scene33 vary, in the romantic lifelikeness of the action, in the mixture of comedy with serious matter, in the gorgeousness of the poetry and the direct appeal to the feelings, both these great literatures closely resemble each other.
Yet the differences, though they do not strike us so readily as the similarities, are yet more34 vital and go deeper; for the similarities are of form, the differences of spirit.
The Elizabethan drama was a great popular literature which aimed at a vigorous and realistic presentation of life and character such as would please a mixed and not very critical audience; it had therefore the strength and weakness of great popular literature; its strength was an abounding vigour in passion and action, and an unequalled grasp upon life; its weakness a crude violence, imperfection and bungling in workmanship combined with a tendency to exaggerations, horrors and monstrosities.
The Hindu drama, on the contrary, was written by men of accomplished culture35 for an educated, often a courtly audience and with an eye to an elaborate and well-understood system of poetics.
Elizabethan.
In the mixture of prose and poetry, in the complete freedom with which time and scene33 vary, in the romantic lifelikeness of the action, in the mixture of comedy with serious matter, in the gorgeousness of the poetry and the direct appeal to the feelings, both these great literatures closely resemble each other.
Yet the differences, though they do not strike us so readily as the similarities, are yet more34 vital and go deeper; for the similarities are of form, the differences of spirit.
The Elizabethan drama was a great popular literature which aimed at a vigorous and realistic presentation of life and character such as would please a mixed and not very critical audience; it had therefore the strength and weakness of great popular literature; its strength was an abounding vigour in passion and action, and an unequalled grasp upon life; its weakness a crude violence, imperfection and bungling in workmanship combined with a tendency to exaggerations, horrors and monstrosities.
The Hindu drama, on the contrary, was written by men of accomplished culture35 for an educated, often a courtly audience and with an eye to an elaborate and well-understood system of poetics.
The36
vital law governing Hindu poetics is that it does not seek to represent life and
character primarily or for their own sake; its aim is fundamentally aesthetic,
by the delicate and harmonious rendering of passion to awaken37 the aesthetic sense of the onlooker and gratify it by moving or38 subtly observed pictures of human feeling; it did not attempt to seize a man’s spirit by the hair and drag it out into a storm of horror and pity and fear and return it to him drenched, beaten and shuddering.
To the Hindu it would have seemed a savage and inhuman spirit that could take any aesthetic pleasure in the sufferings of an Oedipus or a Duchess of Malfi or in the tragedy of a Macbeth or an Othello.
Partly this arose from the divine tenderness of the Hindu nature, always noble, forbearing and gentle and at that time saturated with the sweet and gracious pity and purity which flowed from the soul of Buddha; but it was also a necessary result of the principle that aesthetic and intellectual pleasure is the first object of all poetic art.
Certainly poetry was regarded as a force for elevation as well as for charm, but as it reaches these 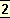
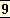
 objects through aesthetic beauty, aesthetic gratification must be the whole basis of dramatic composition; all other objects are superstructural39.
The Hindu mind therefore shrank not only from violence, horror and physical tragedy, the Elizabethan stock-in-trade, but even from the tragic moral40 problems which attracted the Greek mind; still less could it have consented to occupy itself with the problems of disease, neurosis and spiritual medicology generally which are the staple of modern drama and fiction.
An atmosphere of romantic beauty, a high urbanity and a gracious equipoise of the feelings, a perpetual confidence in the sunshine and the flowers, are the essential spirit of a Hindu play; pity and terror are used to awaken the feelings, but not to lacerate them, and the drama must close on the note of joy and peace; the clouds are only admitted to make more beautiful the glad sunlight from which all came and into which all must melt away.
It is in an art like this that the soul finds the repose, the opportunity for being, confirmed in gentleness and in kindly culture, the unmixed intellectual and aesthetic pleasure in quest of which it has turned41 away from the crudeness and incoherence of life to the magic regions of Art.
objects through aesthetic beauty, aesthetic gratification must be the whole basis of dramatic composition; all other objects are superstructural39.
The Hindu mind therefore shrank not only from violence, horror and physical tragedy, the Elizabethan stock-in-trade, but even from the tragic moral40 problems which attracted the Greek mind; still less could it have consented to occupy itself with the problems of disease, neurosis and spiritual medicology generally which are the staple of modern drama and fiction.
An atmosphere of romantic beauty, a high urbanity and a gracious equipoise of the feelings, a perpetual confidence in the sunshine and the flowers, are the essential spirit of a Hindu play; pity and terror are used to awaken the feelings, but not to lacerate them, and the drama must close on the note of joy and peace; the clouds are only admitted to make more beautiful the glad sunlight from which all came and into which all must melt away.
It is in an art like this that the soul finds the repose, the opportunity for being, confirmed in gentleness and in kindly culture, the unmixed intellectual and aesthetic pleasure in quest of which it has turned41 away from the crudeness and incoherence of life to the magic regions of Art.
When therefore English scholars, fed on the exceedingly strong and often raw meat of the Elizabethans, assert that there are no characters in the Hindu drama, when they attribute this deficiency to the feebleness of inventive power which leads “Asiatic” poetry to concentrate itself on glowing description and imagery, seeking by excess42 of ornament to conceal poverty of substance, when even their Indian pupils perverted from good taste and blinded to fine discrimination by a love of the striking and a habit of gross forms and pronounced colours due to the too exclusive study of English poetry, repeat and reenforce43 their criticisms, the lover of Kalidasa and his peers need not be alarmed; he need not banish from his imagination the gracious company with which it is peopled as a gilded and soulless list of names44.
For these45 dicta spring from prejudice and the echo of a prejudice; they are evidence not of a more vigorous critical mind but of a restricted critical sympathy.
Certainly if46 we expect a Beautiful White Devil or a Jew of Malta from the Hindu dramatist, we 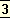
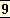
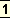
 shall be disappointed; he deals not in these splendid or horrible masks.
If we come to him for a Lear or a Macbeth, we shall go away discontented; for these also are sublimities which belong to cruder civilisations and more barbarous national types; in worst crimes and deepest47 suffering as well as in happiness48 and virtue, the Aryan was more civilized and temperate, less crudely enormous than the hard, earthy and material African49 peoples whom in Europe he only half moralised.
If he seeks a Père Goriot or a Madame Bovary, he will still fail in his quest; for though such types doubtless existed at all times among the mass of the people with its50 large strain of African blood, Hindu Art would have shrunk from poisoning the moral atmosphere of the soul by elaborate studies of depravity.
The true spirit of criticism is to seek in a literature what we can find in it of great or beautiful, not to demand from it what it does not seek to give us.
shall be disappointed; he deals not in these splendid or horrible masks.
If we come to him for a Lear or a Macbeth, we shall go away discontented; for these also are sublimities which belong to cruder civilisations and more barbarous national types; in worst crimes and deepest47 suffering as well as in happiness48 and virtue, the Aryan was more civilized and temperate, less crudely enormous than the hard, earthy and material African49 peoples whom in Europe he only half moralised.
If he seeks a Père Goriot or a Madame Bovary, he will still fail in his quest; for though such types doubtless existed at all times among the mass of the people with its50 large strain of African blood, Hindu Art would have shrunk from poisoning the moral atmosphere of the soul by elaborate studies of depravity.
The true spirit of criticism is to seek in a literature what we can find in it of great or beautiful, not to demand from it what it does not seek to give us.
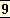
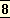
 This contradiction, violent as it is, is not difficult to understand, since it takes its root in an element always more or less present in criticism, the national element.
National character12, national prejudices, national training preordain for the bulk of us the spirit in which we shall approach13 unfamiliar poetry.
Now the average English mind is capable of appreciating character as manifested in strong action or powerfully revealing speech, but constitutionally dull to the subtleties of civilized14 character15 which have their theatre in the mind and the heart and make of a slight word, a gesture or even silence their sufficient revelation.
The nations of Europe, taken in the mass, are still semicivilized; their mind feeds on the physical, external and grossly salient features of life; where there is no brilliance and glare, they are apt to condemn the personality16 as characterless.
A strength that shuns ostentation, a charm that is not luxuriant, not naked to the first glance, are appreciable only to the few select minds who have chastened their natural leanings by a wide and deep culture.
The Hindu on his side distastes17 violence in action, excess in speech, ostentation or effusiveness in manner; he demands from his ideal temperance and restraint as well as nobility, truth and beneficence; the Aryan or true gentleman must be मिताचारः (mitācāraḥ) and मितभाषी, (mitābhāṣī) restrained in action and temperate in speech.
This contradiction, violent as it is, is not difficult to understand, since it takes its root in an element always more or less present in criticism, the national element.
National character12, national prejudices, national training preordain for the bulk of us the spirit in which we shall approach13 unfamiliar poetry.
Now the average English mind is capable of appreciating character as manifested in strong action or powerfully revealing speech, but constitutionally dull to the subtleties of civilized14 character15 which have their theatre in the mind and the heart and make of a slight word, a gesture or even silence their sufficient revelation.
The nations of Europe, taken in the mass, are still semicivilized; their mind feeds on the physical, external and grossly salient features of life; where there is no brilliance and glare, they are apt to condemn the personality16 as characterless.
A strength that shuns ostentation, a charm that is not luxuriant, not naked to the first glance, are appreciable only to the few select minds who have chastened their natural leanings by a wide and deep culture.
The Hindu on his side distastes17 violence in action, excess in speech, ostentation or effusiveness in manner; he demands from his ideal temperance and restraint as well as nobility, truth and beneficence; the Aryan or true gentleman must be मिताचारः (mitācāraḥ) and मितभाषी, (mitābhāṣī) restrained in action and temperate in speech.