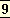Sri Aurobindo
Essays Divine and Human
Writings from Manuscripts. 1910 – 1950
The Problem of Consciousness
What is Consciousness?
85
Consciousness — but what is consciousness?
A word only conveniently ticketing a class1 of natural phenomena or a fundamental reality of existence?
Apparently a phenomenon which has only a small range intervening in an immense mass of things inconscient and without significance, consciousness alone gives a value to the universe.
It 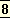
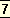
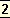
 seems to have taken no part in the creation of the universe; it was not there in the beginning or even during the greater part of the history of the earth; it may not be there at its end.
In the middle it plays a great role in the life of animal and man, but its action is crude and ill-developed in the animal, imperfect in the human creature.
Its evolution wears the character of an episode in the long history of an inconscient world, a chapter that began some time ago, but one knows not why it intervened at all or how it will end2 or whether its appearance has any meaning, whether its developing importance has an accidental and meaningless or a purposeful and revelatory character.
It may be a freak of creative Chance or it may be or may carry in itself the whole meaning of the world-drama.
seems to have taken no part in the creation of the universe; it was not there in the beginning or even during the greater part of the history of the earth; it may not be there at its end.
In the middle it plays a great role in the life of animal and man, but its action is crude and ill-developed in the animal, imperfect in the human creature.
Its evolution wears the character of an episode in the long history of an inconscient world, a chapter that began some time ago, but one knows not why it intervened at all or how it will end2 or whether its appearance has any meaning, whether its developing importance has an accidental and meaningless or a purposeful and revelatory character.
It may be a freak of creative Chance or it may be or may carry in itself the whole meaning of the world-drama.
In an inconscient universe, in a Nature or the working of an Energy which is fundamentally material, the emergence [of] Consciousness has at first the air of a surprising, a contradictory, an impossible event.
For in such a world, in the working of such a Nature or Energy, how could it ever come into existence?
Either there is no real consciousness, only an action of Matter or unconscious Energy which takes this inexplicable and deceptive form, or Nature or Energy is not fundamentally inconscient.
Consciousness was always a possibility which at a certain stage chanced or was bound to take place, or it was a latent power that has become manifest.
Or even it may be all Nature is really conscious and it is we who foist inconscience upon her because we are limited to a certain range and character of consciousness and cannot communicate with her other ranges or even detect their existence.
It has been held by a certain opinion that consciousness in itself does not exist, there are only phenomena of reactions of Matter to Matter or of Energy in Matter to Energy in Matter to which by generalisation we give the name.
There is no person who is conscious, thinks, speaks, perceives, wills, acts; it is an organised body in which certain chemical, molecular, cellular, glandular and nerve activities take place and certain material results and reactions of these activities take place in the brain which take the form of these phenomena.
It is the 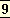
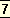
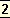
 body that thinks, perceives, wills, speaks, acts; it is Matter that goes through these operations and becomes aware of them; it may be said that brain-matter makes a record or notation of these actions and this notation is consciousness and this record is memory.
There is nothing in the world except Matter and the operations of Matter.
body that thinks, perceives, wills, speaks, acts; it is Matter that goes through these operations and becomes aware of them; it may be said that brain-matter makes a record or notation of these actions and this notation is consciousness and this record is memory.
There is nothing in the world except Matter and the operations of Matter.
This theory arose when physical Science concentrated on the operations of Matter, saw only Matter and energy of Matter everywhere; it persists even after that seeing of things has been severely shaken.
For now we are driven to see and say that there is no such thing as Matter in itself; what we call Matter is only a mass of phenomena of Energy, events of energy, which our senses regard as objects and our minds classify under the general name of Matter.
But we can still hold that all phenomena are phenomena of Energy acting in the forms or sensible events which we call Matter and the phenomena of consciousness are of that character.
There is nothing else to it, nothing but the mobile and executive Energy, Nature, Prakriti; there is no soul, no Purusha.
Consciousness would still be a general name for a brain-record and notation of these events of material Energy and this will still be the true character of thought, perception, will, speech, act.
All these events are separate phenomena which may act and react on each other or group themselves together, but they are not the result or manifestations of any one general force or power of being that we can call Consciousness.
Circa 1937/43
{DocumentDescription}
{StartingDate}
{Year}
1937
{/Year}
{Exactness}
Circa
{/Exactness}
{/StartingDate}
{EndingDate}
{Year}
1943
{/Year}
{Exactness}
Circa
{/Exactness}
{/EndingDate}
{DateType}
Writting
{/DateType}
{WorkKind}
Manuscript
{/WorkKind}
{/DocumentDescription}
 seems to have taken no part in the creation of the universe; it was not there in the beginning or even during the greater part of the history of the earth; it may not be there at its end.
In the middle it plays a great role in the life of animal and man, but its action is crude and ill-developed in the animal, imperfect in the human creature.
Its evolution wears the character of an episode in the long history of an inconscient world, a chapter that began some time ago, but one knows not why it intervened at all or how it will end2 or whether its appearance has any meaning, whether its developing importance has an accidental and meaningless or a purposeful and revelatory character.
It may be a freak of creative Chance or it may be or may carry in itself the whole meaning of the world-drama.
seems to have taken no part in the creation of the universe; it was not there in the beginning or even during the greater part of the history of the earth; it may not be there at its end.
In the middle it plays a great role in the life of animal and man, but its action is crude and ill-developed in the animal, imperfect in the human creature.
Its evolution wears the character of an episode in the long history of an inconscient world, a chapter that began some time ago, but one knows not why it intervened at all or how it will end2 or whether its appearance has any meaning, whether its developing importance has an accidental and meaningless or a purposeful and revelatory character.
It may be a freak of creative Chance or it may be or may carry in itself the whole meaning of the world-drama.