Sri Aurobindo
Letters on Poetry and Art
SABCL - Volume 27
Part 2. On His Own and Others’ Poetry
Section 2. On Poets and Poetry
Indian Poetry in English
On Some Indian Writers of English [2]
The idea that Indians cannot succeed in English poetry
is very much in the air just now but it cannot be taken as absolutely valid.
Toru Dutt and Romesh of the same ilk prove nothing; Toru Dutt was an
accomplished verse-builder with a delicate talent and some outbreaks of genius
and she wrote things that were attractive and sometimes something that had a
strong energy of language and a rhythmic force. Romesh was a smart imitator of
English poetry of the second or third rank. What he wrote, if written by an
Englishman, might not have had even a temporary success. Sarojini is different.
Her work has a real beauty, but it has for the most part only one highly lyrical
note and a vein of riches that has been soon exhausted. Some of her lyrical work
is likely, I think, to survive among the lasting things in English literature
and by these, even if they are fine rather than great, she 
 may take her rank among the immortals. I know no other Indian poets
who have published in English anything that is really alive and strong and
{{0}}original.[[This was written some years ago and does not apply to more
recent work in English by Indian poets.]] The test will be when something is
done that is of real power and scope and gets its due chance. Tagore’s
Gitanjali is not in verse, but the place it has taken has some significance.
For the obstacles from the other side are that the English mind is apt to look
on poetry by an Indian as a curiosity, something exotic (whether it really is or
not, the suggestion will be there), and to stress the distance at which the
English temperament stands from the Indian temperament. But Tagore’s
Gitanjali is most un-English, yet it overcame this obstacle. For the poetry
of spiritual experience, even if it has true poetic value, the difficulty might
lie in the remoteness of the subject. But nowadays this difficulty is lessening
with the increasing interest in the spiritual and the mystic. It is an age in
which Donne, once condemned as a talented but fantastic weaver of extraordinary
conceits, is being hailed as a great poet, and Blake lifted to a high eminence;
even small poets with the mystic turn are being pulled out of their obscurity
and held up to the light. At present many are turning to India for its sources
of spirituality, but the eye has been directed only towards yoga and philosophy,
not to the poetical expression of it. When the full day comes, however, it may
well be that this too will be discovered, and then an Indian who is at once a
mystic and a true poet and able to write in English as if in his mother-tongue
(that is essential) would have his full chance. Many barriers are breaking;
moreover both in French and English there are instances of foreigners who have
taken their place whether as prose-writers or poets.
may take her rank among the immortals. I know no other Indian poets
who have published in English anything that is really alive and strong and
{{0}}original.[[This was written some years ago and does not apply to more
recent work in English by Indian poets.]] The test will be when something is
done that is of real power and scope and gets its due chance. Tagore’s
Gitanjali is not in verse, but the place it has taken has some significance.
For the obstacles from the other side are that the English mind is apt to look
on poetry by an Indian as a curiosity, something exotic (whether it really is or
not, the suggestion will be there), and to stress the distance at which the
English temperament stands from the Indian temperament. But Tagore’s
Gitanjali is most un-English, yet it overcame this obstacle. For the poetry
of spiritual experience, even if it has true poetic value, the difficulty might
lie in the remoteness of the subject. But nowadays this difficulty is lessening
with the increasing interest in the spiritual and the mystic. It is an age in
which Donne, once condemned as a talented but fantastic weaver of extraordinary
conceits, is being hailed as a great poet, and Blake lifted to a high eminence;
even small poets with the mystic turn are being pulled out of their obscurity
and held up to the light. At present many are turning to India for its sources
of spirituality, but the eye has been directed only towards yoga and philosophy,
not to the poetical expression of it. When the full day comes, however, it may
well be that this too will be discovered, and then an Indian who is at once a
mystic and a true poet and able to write in English as if in his mother-tongue
(that is essential) would have his full chance. Many barriers are breaking;
moreover both in French and English there are instances of foreigners who have
taken their place whether as prose-writers or poets.
P.S. About decadence: a language becomes decadent when
the race decays, when life and soul go out and only the dry intellect and the
tired senses remain. Europe is in imminent peril of decadence and all its
literatures are attacked by this malady, though it is only beginning and energy
is still there which may 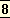
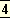
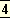
 bring renewal. But the
English language has still several strings to its bow and is not confined to an
aged worn-out England. Moreover, there are two tendencies active in the modern
mind, the over-intellectualised, over-sensualised decadent that makes for death,
and the spiritual which may bring rebirth. At present the decadent tendency may
be stronger, but the other is also there.
bring renewal. But the
English language has still several strings to its bow and is not confined to an
aged worn-out England. Moreover, there are two tendencies active in the modern
mind, the over-intellectualised, over-sensualised decadent that makes for death,
and the spiritual which may bring rebirth. At present the decadent tendency may
be stronger, but the other is also there.
24 January 1935
 may take her rank among the immortals. I know no other Indian poets
who have published in English anything that is really alive and strong and
{{0}}original.[[This was written some years ago and does not apply to more
recent work in English by Indian poets.]] The test will be when something is
done that is of real power and scope and gets its due chance. Tagore’s
Gitanjali is not in verse, but the place it has taken has some significance.
For the obstacles from the other side are that the English mind is apt to look
on poetry by an Indian as a curiosity, something exotic (whether it really is or
not, the suggestion will be there), and to stress the distance at which the
English temperament stands from the Indian temperament. But Tagore’s
Gitanjali is most un-English, yet it overcame this obstacle. For the poetry
of spiritual experience, even if it has true poetic value, the difficulty might
lie in the remoteness of the subject. But nowadays this difficulty is lessening
with the increasing interest in the spiritual and the mystic. It is an age in
which Donne, once condemned as a talented but fantastic weaver of extraordinary
conceits, is being hailed as a great poet, and Blake lifted to a high eminence;
even small poets with the mystic turn are being pulled out of their obscurity
and held up to the light. At present many are turning to India for its sources
of spirituality, but the eye has been directed only towards yoga and philosophy,
not to the poetical expression of it. When the full day comes, however, it may
well be that this too will be discovered, and then an Indian who is at once a
mystic and a true poet and able to write in English as if in his mother-tongue
(that is essential) would have his full chance. Many barriers are breaking;
moreover both in French and English there are instances of foreigners who have
taken their place whether as prose-writers or poets.
may take her rank among the immortals. I know no other Indian poets
who have published in English anything that is really alive and strong and
{{0}}original.[[This was written some years ago and does not apply to more
recent work in English by Indian poets.]] The test will be when something is
done that is of real power and scope and gets its due chance. Tagore’s
Gitanjali is not in verse, but the place it has taken has some significance.
For the obstacles from the other side are that the English mind is apt to look
on poetry by an Indian as a curiosity, something exotic (whether it really is or
not, the suggestion will be there), and to stress the distance at which the
English temperament stands from the Indian temperament. But Tagore’s
Gitanjali is most un-English, yet it overcame this obstacle. For the poetry
of spiritual experience, even if it has true poetic value, the difficulty might
lie in the remoteness of the subject. But nowadays this difficulty is lessening
with the increasing interest in the spiritual and the mystic. It is an age in
which Donne, once condemned as a talented but fantastic weaver of extraordinary
conceits, is being hailed as a great poet, and Blake lifted to a high eminence;
even small poets with the mystic turn are being pulled out of their obscurity
and held up to the light. At present many are turning to India for its sources
of spirituality, but the eye has been directed only towards yoga and philosophy,
not to the poetical expression of it. When the full day comes, however, it may
well be that this too will be discovered, and then an Indian who is at once a
mystic and a true poet and able to write in English as if in his mother-tongue
(that is essential) would have his full chance. Many barriers are breaking;
moreover both in French and English there are instances of foreigners who have
taken their place whether as prose-writers or poets.